Book-Keeping
Book-keeping is the systematic recording of financial transactions. It involves recording daily business activities such as sales, purchases, expenses, and receipts. The primary purpose of book-keeping is to maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records.
![![enter image description here][1]](https://santoshtandukar.com.np/content/images/20241102095450-1000010582.png)
Key Components of Book-Keeping
- Journal: A chronological record of all financial transactions.
- Ledger: A book of accounts where transactions are classified and summarized.
- Trial Balance: A statement that verifies the equality of debits and credits in the ledger.
Accounting
Accounting is the process of analyzing, interpreting, and communicating financial information. It involves recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing, and interpreting financial transactions to provide a clear picture of a business's financial health.
Branches of Accounting
- Financial Accounting: Concerned with preparing financial statements for external users like investors, creditors, and government agencies.
- Management Accounting: Provides financial information to internal users like managers to aid in decision-making.
- Cost Accounting: Focuses on recording, classifying, and analyzing costs to help in decision-making and cost control.
Accounting Cycle
The accounting cycle is a series of steps involved in processing financial transactions. It includes:
- Journalizing: Recording transactions in the journal.
- Posting: Transferring journal entries to the ledger.
- Preparing a Trial Balance: Verifying the equality of debits and credits.
- Adjusting Entries: Recording adjusting entries to update accounts.
- Preparing an Adjusted Trial Balance: Verifying the equality of debits and credits after adjustments.
- Preparing Financial Statements: Creating the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
- Closing the Books: Transferring net income or loss and temporary accounts to retained earnings.
- Post-Closing Trial Balance: Verifying the equality of debits and credits after closing entries.
Final Accounts
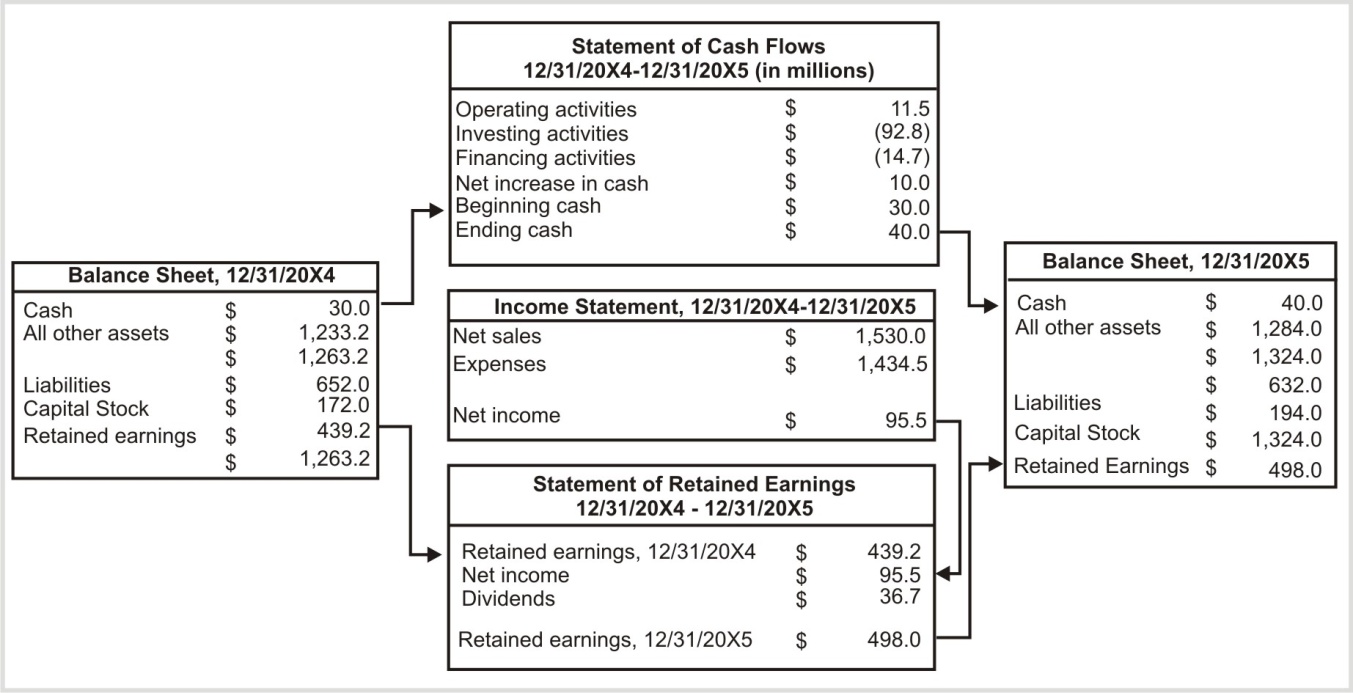
Final accounts are the culmination of the accounting process and provide a comprehensive view of a business's financial performance. They typically include:
- Income Statement: Shows the revenue and expenses of a business over a specific period.
- Balance Sheet: Presents a snapshot of a business's financial position at a particular point in time.
- Cash Flow Statement: Reveals the inflows and outflows of cash during a specific period.
Importance of Book-Keeping and Accounting
- Financial Health Assessment: Provides insights into a business's financial performance.
- Decision-Making: Aids in informed decision-making by providing accurate financial data.
- Tax Compliance: Helps in accurate tax filing and compliance with tax regulations.
- Investor Confidence: Inspires confidence in investors by providing transparent financial information.
- Risk Management: Identifies potential financial risks and helps in risk mitigation.
Conclusion
Book-keeping and accounting are essential tools for businesses of all sizes. By maintaining accurate financial records and analyzing financial data, businesses can make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and achieve long-term success.
Additional Tips for Effective Book-Keeping and Accounting
- Use Accounting Software: Utilize accounting software to streamline processes and reduce errors.
- Regularly Reconcile Accounts: Ensure accuracy by reconciling bank accounts and other financial records.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with an accountant or financial advisor for complex financial matters.
- Stay Updated on Accounting Standards: Keep up-to-date with the latest accounting standards and regulations.
- Maintain Organized Records: Keep all financial documents organized and easily accessible.
By following these tips and principles, businesses can establish strong financial foundations and achieve sustainable growth.
Here are a few suggestions:
Financial Accounting:
- Ratio Analysis: Understanding financial ratios like liquidity, solvency, profitability, and efficiency.
- Inventory Valuation Methods: Exploring different methods like FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average.
- Revenue Recognition: Understanding the principles and standards for recognizing revenue.
Management Accounting:
- Cost Accounting: Analyzing different cost concepts like direct costs, indirect costs, fixed costs, and variable costs.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Creating budgets, forecasting future performance, and variance analysis.
- Performance Measurement: Using KPIs and other metrics to evaluate performance.
Other Topics:
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS): Exploring the global standards for financial reporting.
- Tax Accounting: Understanding tax laws, regulations, and implications for businesses.
- Auditing: The process of examining financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance.