Transfer pricing harmonization refers to the efforts to align transfer pricing rules and regulations across different countries. This is important because it can help to reduce double taxation and promote international trade.
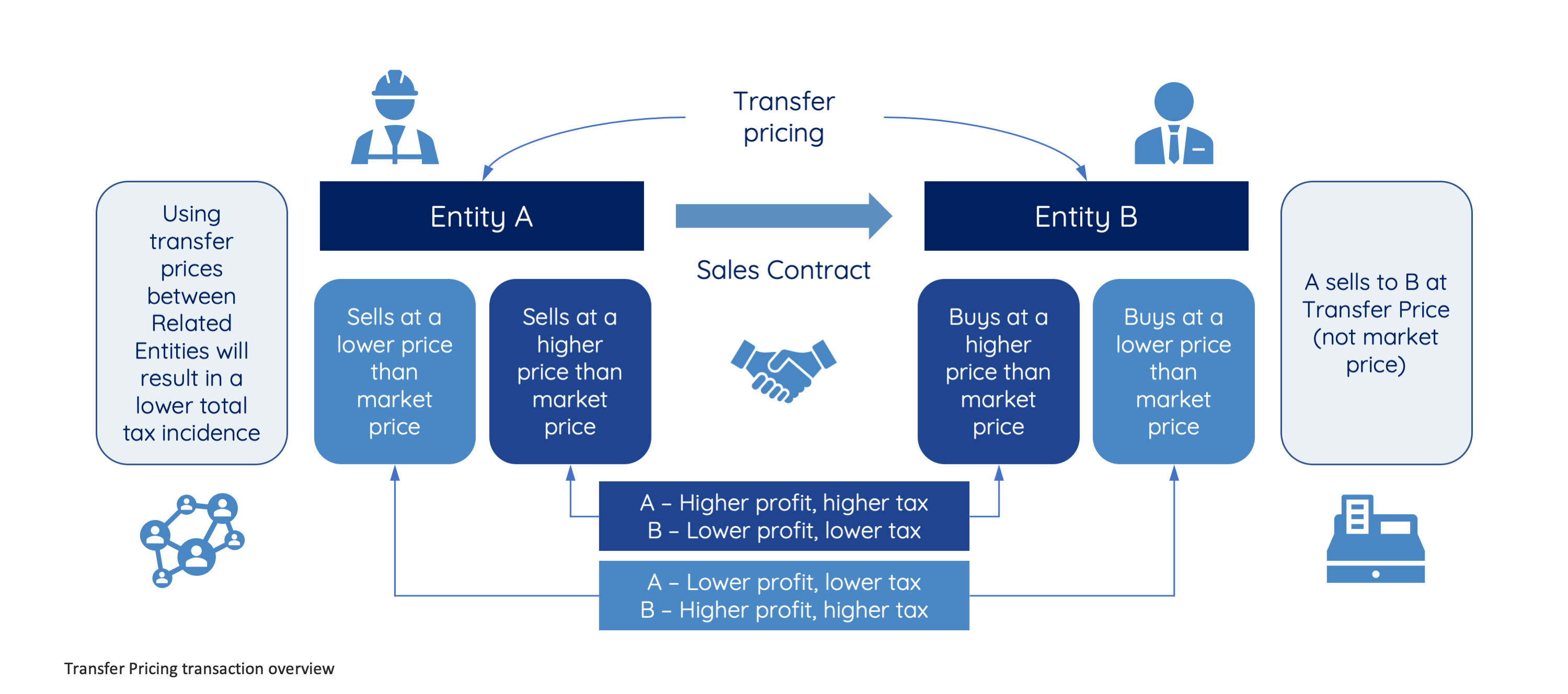
Transfer Pricing (TP) refers to the value of transactions between related parties, often influenced by a group's interests rather than market forces. Companies may manipulate prices to shift profits to lower-tax jurisdictions, reducing taxes in higher-tax countries. To address this, a TP directive has been issued to ensure that transactions between related multinational companies are conducted at arm’s length price.
There have been a number of initiatives to harmonize transfer pricing rules. The OECD has published a Transfer Pricing Guidelines that provide guidance to governments on how to develop and implement transfer pricing rules. The UN has also published a Transfer Pricing Manual that provides guidance to developing countries.
While there has been some progress in harmonizing transfer pricing rules, there are still significant differences between the rules of different countries. This can make it difficult for businesses to comply with the rules and can increase their tax compliance costs.
It is important to consult with a tax professional to ensure that your company's transfer pricing practices are compliant with the law.
Transfer pricing benchmarking involves comparing the prices of transactions between related parties to the prices of comparable transactions between unrelated parties. This can be done using a variety of methods, including:
- Comparable uncontrolled price (CUP) method: Compares the price of the transaction to the price of a comparable transaction between unrelated parties.
- Resale price method: Calculates the price based on the resale price of the property by the related party.
- Cost plus method: Calculates the price based on the cost of producing the property plus a reasonable profit margin.
- Profit split method: Allocates profits between related parties based on their relative contributions to the transaction.
Benchmarking can be a complex process, and it is important to consult with a tax professional to ensure that your company's transfer pricing practices are compliant with the law.