Financial statements are formal records of a company’s financial activities, providing insights into its financial position, performance, and cash flows. They are essential for stakeholders like management, investors, creditors, and regulators to make informed decisions. There are four main financial statements:
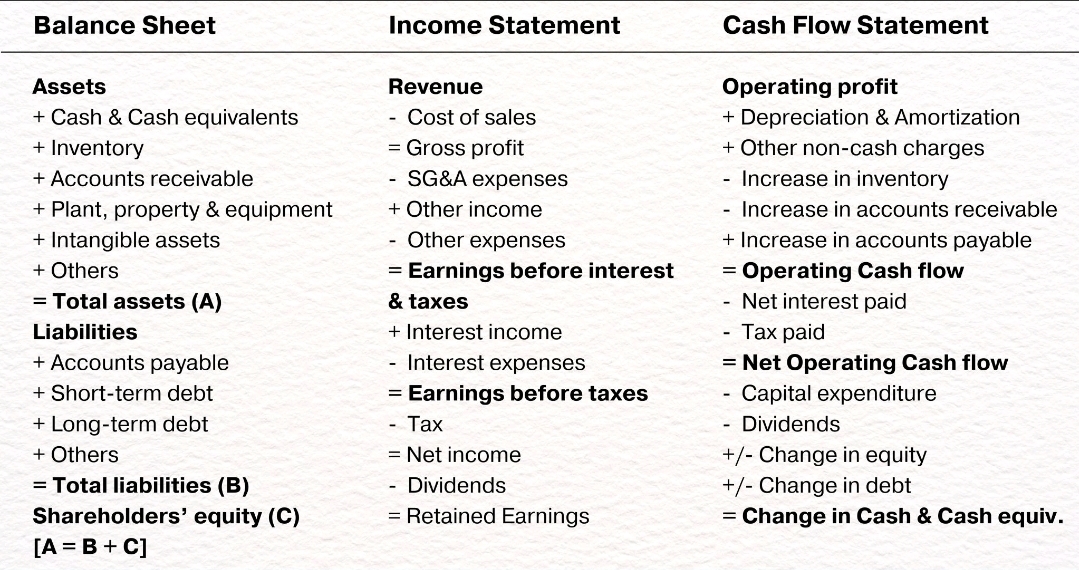
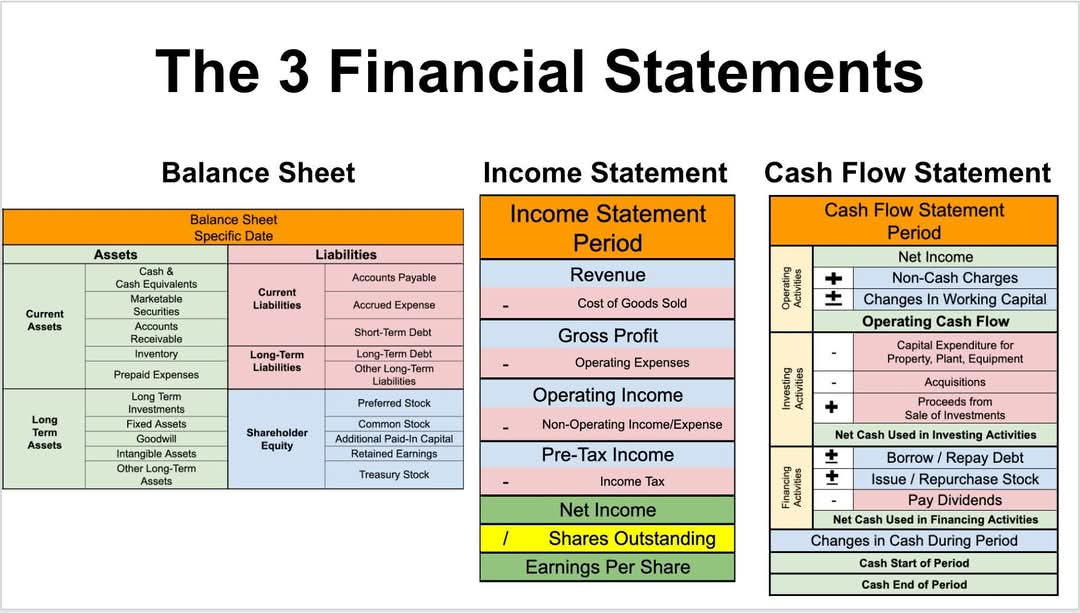
1. Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position):
Purpose: Shows a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
Components:
Assets: What the company owns, such as cash, inventory, property, and receivables.
Liabilities: What the company owes, such as loans, accounts payable, and other debts.
Equity: Owners’ interest in the company, including retained earnings and contributed capital.
Formula: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Significance: It highlights the company’s solvency and liquidity by presenting its resources and obligations.
2. Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement):
Purpose: Shows a company’s financial performance over a specific period (monthly, quarterly, or annually).
Components:
Revenue: Income earned from sales or services provided.
Expenses: Costs incurred to generate revenue (e.g., salaries, rent, cost of goods sold).
Profit (Net Income): Calculated as revenue minus expenses.
Formula: Net Income = Revenue - Expenses
Significance: It provides insight into a company’s profitability and efficiency in generating profit from operations.
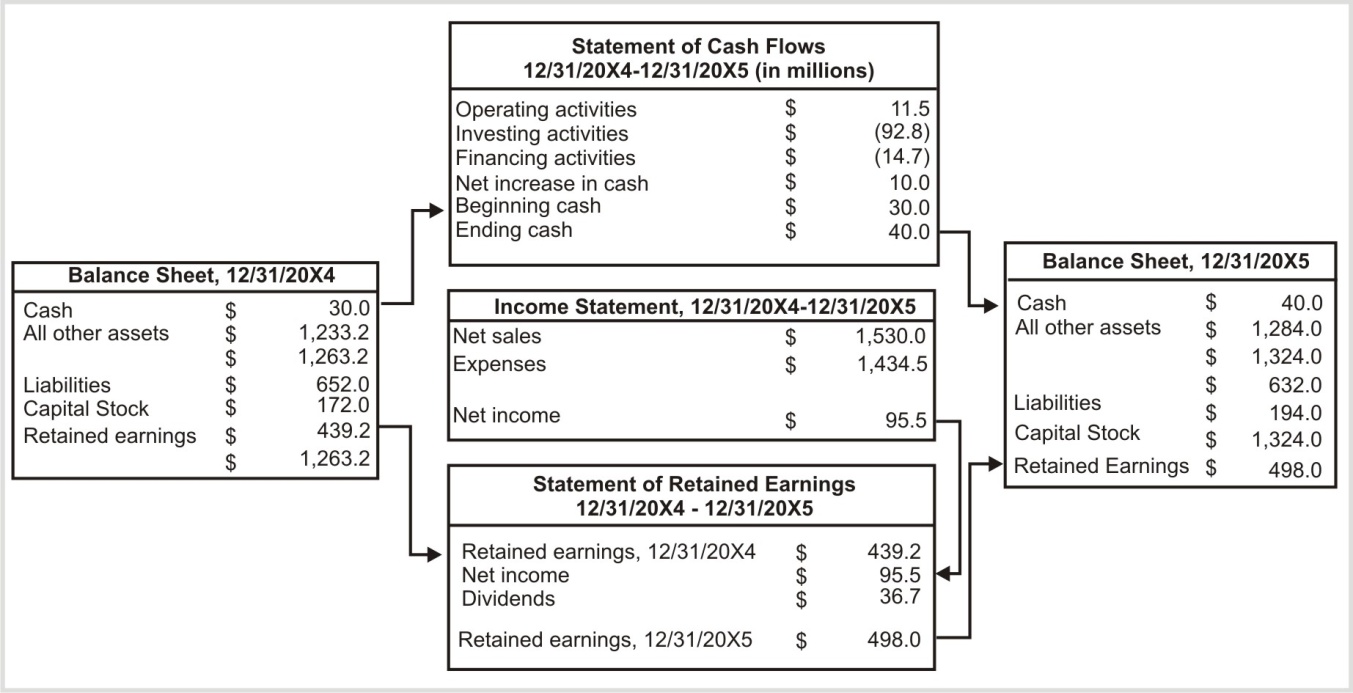
3. Cash Flow Statement:
Purpose: Details the cash inflows and outflows over a specific period, showing how cash is generated and used.
Components:
Operating Activities: Cash flows from core business operations (sales, operating expenses).
Investing Activities: Cash flows from buying or selling long-term assets (property, equipment, investments).
Financing Activities: Cash flows from borrowing, repaying debt, issuing shares, and paying dividends.
Formula: Net Cash Flow = Cash Inflows - Cash Outflows
Significance: It reveals the company’s liquidity and its ability to manage cash for operations, investments, and financing.
4. Statement of Changes in Equity (Statement of Retained Earnings):
Purpose: Shows the changes in owners’ equity over a period.
Components:
Contributed Capital: The amount invested by owners or shareholders.
Retained Earnings: Cumulative earnings retained in the business after dividends.
Other Comprehensive Income: Changes due to other gains/losses not reflected in the income statement.
Significance: It provides insight into how net income, dividends, and other changes affect shareholders' equity.
Summary:
Financial statements provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health. The balance sheet reflects its financial position, the income statement shows profitability, the cash flow statement illustrates cash management, and the statement of changes in equity highlights changes in ownership value. Together, they are vital tools for decision-making, assessing risks, and strategic planning.