Statement of Shareholders' Equity
The Statement of Shareholders' Equity (also known as the Statement of Changes in Equity) is a financial statement that outlines the changes in a company's equity during a specific period. It provides insights into how the company’s net worth has evolved due to operations, investments, and financing activities.
Objectives of the Statement of Shareholders’ Equity
Track Equity Changes: Shows the movement in shareholders' equity accounts over a period.
Transparency: Provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of the factors affecting the company's equity.
Performance Evaluation: Highlights how retained earnings, dividends, and other factors contribute to equity.
Investor Confidence: Assures shareholders about the company’s financial stability and growth prospects.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to financial reporting standards.
Elements of the Statement of Shareholders’ Equity
- Common Stock:
Represents the initial and additional funds invested by shareholders in exchange for ownership.
Includes both par value and any additional paid-in capital.
- Preferred Stock:
The equity issued to preferred shareholders with priority over common shareholders in dividends and liquidation.
- Additional Paid-In Capital (APIC):
Excess funds received from shareholders over and above the par value of stock issued.
- Retained Earnings:
Accumulated profits or losses retained in the company after paying dividends.
Formula: Retained Earnings (End) = Retained Earnings (Start) + Net Income - Dividends.
- Treasury Stock:
Shares repurchased by the company, reducing equity as these are not outstanding.
Recorded as a negative figure in equity.
- Other Comprehensive Income (OCI):
Items that bypass the income statement, such as unrealized gains/losses on investments, foreign currency translations, or pension adjustments.
- Non-Controlling Interest (if applicable):
Equity attributable to minority shareholders in subsidiaries, if the company consolidates results.
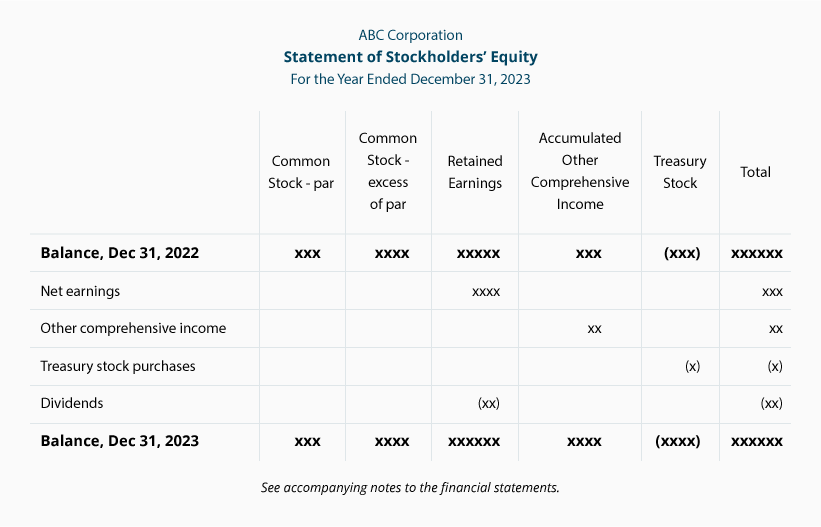
Structure of the Statement of Shareholders’ Equity
Importance and Analysis
- Investor Decision-Making:
Investors can assess profitability and dividend policies.
- Company Stability:
Highlights the company’s ability to grow and maintain positive equity.
- Capital Management:
Reflects how effectively the company utilizes and manages its equity.
- Risk Assessment:
A decline in equity over time might signal financial instability.
Conclusion
The Statement of Shareholders’ Equity is a critical component of financial reporting that provides an overview of changes in ownership and equity during a given period. By analyzing this statement, stakeholders gain a deeper understanding of the company’s financial health, investment potential, and overall performance.